Investigation of the Cytotoxic and Genotoxic Effects of the Euphorbia rigida Bieb. Extract
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.13128/caryologia-1029Keywords:
Allium test, Biopesticide, Cell aberrations, Cytotoxic, Genotoxic and Euphorbia rigida Bieb.Abstract
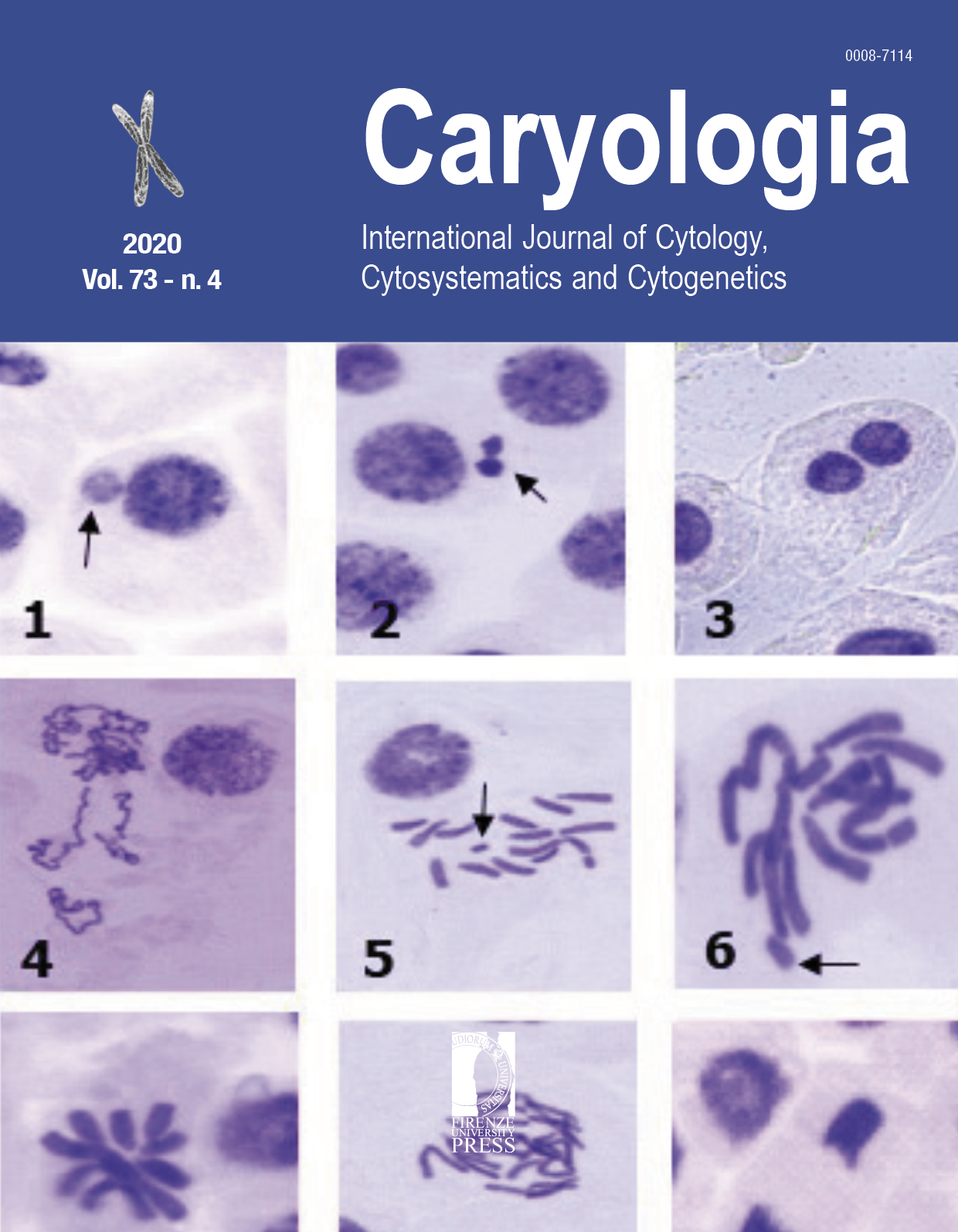
The present study was conducted to evaluate and compare the cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of the aqueous extracts of Euphorbia rigida Bieb. which is a natural pesticide. The comparison was done using the Allium test to the chemical pesticides Elandor® and Goldplan®. According to Allium test results, it had negative impacts on mitosis and showed cytotoxic and genotoxic effects on the existing cells. The lowest level of MI (2.95 %) was observed in the 200 ppm treatment of E. rigida extract. Number of the aberrant cells were 88.1, 84.1 and 82.5 in the treatments with Elandor®, 50 ppm, E. rigida extract and Goldplan® respectively. The highest cytological anomalies were chromosome stickiness, irregular metaphase and anaphase, pole deviations and C-mitosis. According to the present results of this research, we can suggest that the extract obtained from E. rigida plant with water up to 50 ppm can be used as an alternative to chemicals used as biopesticide. Antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral properties of Euphorbia extracts are well known, so it could mean that they can be used as additives or a disinfectant for inanimate surfaces in the pharmaceutics industry. No matter what purposes the extract of this plant is used, great care should be taken while using it because it can cause damage on cells and chromosomes. Hence, through more detailed and comprehensive studies about its capacity for medical and biopesticide purposes should be investigated.
Downloads
References
References
Anonymous. 2013. Euphorbia, the chemical constituents and pharmacological studies. http://eng.hi138.com/?i296401_Euphorbia-the-chemical-constituents-and-pharmacological-studies, 2013, [28.03.2013, h; 15:25].
Adhikari D. 2019. Augmentation mitodepressive and cytogenotoxic effects of lead upon acute exposure on grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) root tip cells. American Journal of Biological Sciences 1(1):14-22.
Ali MS, Ahmed S, Saleem M. 2008. Spirowallichiione: a rearranged multiflorane from Euphorbia wallichii Hook F. (Euphorbiaceae). Molecules, 13, 405-411.
Andrade-Vieira LF, Salabert de Campos JM, Davide LC. 2012. Effects of spent pot liner on mitotic activity and nuclear DNA content in meristematic cells of Allium cepa. J. of Env. M. Volume 107: 140-146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.04.008
Aslantürk Ö, Aşkın-Çelik T. 2013. Antioxidant, cytotoxic and apoptotic activities of extracts from medicinal plant Euphorbia platyphyllos L. J. of Med.Plants Res., Vol.7(19):1293-1304.
Badr A. 1983. Mitodepressive and chromotoxic activities of two herbicides in A. cepa. Cytologia, 48: 451-457.
Başaran AA, Yu T-W, Plewa MJ, Anderson D. 1996. An investigation of some Turkish herbal medicines in Salmonella thyphimurium and in the comet assay in human lymphocytes. Terat. Car. and Mut., 16 (2), 125-138.
Baytop A. 1991. Türkiye’de kullanılan yabani ve yetiştirilmiş aromatik bitkiler. Tr. J. of Pharmacy, 1:76.
Civelek SH. 2003. Ortaca (Muğla) seralarında domateslerde zarar yapan kök ur nematotlarının (Nematoda) ve galeri sineklerinin (Diptera: Agromyzıdae) mücadelesinde bazı bitki ekstraklarının kullanılması üzerine araştırmalar. Muğla Ünv., Bilimsel Araştırma Projeleri, Proje No:00-007 Proje Kesin Raporu.
Civelek HS, Weintraub PG. 2004. Effects of two plant extracts on larval leafminer Liriomyza trifolii (Diptera: Agromyzidae) in tomatoes. J Econ Entomol 97(5): 1581-1586.
Çavuşoğlu F. 2008. Doğu akdeniz bölgesinde yetişen Pinus brutia Ten. ve Quercus coccifera L. yapraklarındaki tanenin antimikrobiyal, mutajenik ve organik madde minerilizasyonuna etkisi. PhD thesis, Çukurova Üniv. Fen Bil. Enst. Biyoloji Ana Bilim Dalı, Adana-Türkiye
Dulkadir K. 2007. Sütleğen (Euphorbia aleppica L.) bitkisinin sekonder metabolitlerinin saflaştırılması, karakterizasyonu ve bazı biyolojik aktivitelerinin belirlenmesi. Master’s thesis, Gaziosmanpaşa Üniv.Fen Bil.Enst, Tokat, Türkiye.
Elçi Ş. 1994. Sitogenetik araştırma yöntemleri ve gözlemler. 100. Yıl Ünv. Yayınları, Yayın No:18, Fen Ed Fak Yayın No:16: 52-83, Van.
Eren Y, Akyıl D, Çalık İ. 2017. Alyssum virgatum Nyar. su ekstrelerinin sitotoksik ve antisitotoksik özellikleri. Iğdır Univ. J. Inst. Sci. & Tech. 7(3): 57-64,
Fiskesjö G. 1981. The allium test on copper in drinking water. Vatten 17(3): 232-240.
Fiskesjö G. 1985. The allium test as a standard in enviromental monitoring. Hereditas 102: 99-112
Grant WF. 1978. Chromosome aberrations in plants as a monitoring system. Environmental Health Perspectives 27: 37–43.
Grisolia CK, Bilich MR, Formigli ML. 2004. A comparative toxicologic and genotoxic study of the herbicide arsenal, its active ıngredient ımazapyr and the surfactant nonylphenol etoxylate. Ecotoxicology and Enviromental Safety 59: 123-126.
Gömürgen AN. 2005. Cytological Effect of the potassium metabisulphite and potassium nitrate food preservative on root tips of Allium cepa L. Cytologia 70(2):119-128. DOI: 10.1508/cytologia.70.119
Güler Ç, Çobanoğlu Z. 1997. Pestisitler, Çevre Sağlığı Kaynak Dizisi No 52, T.C. Sağlık Bakanlığı, İlköz Matbaası, Ankara 1-13, Türkiye.
Huang L, Chen S, Yang M. 2012. Euphorbia hirta (Feiyangcao): a review on its ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J. of Med. Plants Res., Vol. 6(39): 5176-5185.
Kanev MO, Özdemir K, Gökalp FD. 2017. Ergene nehir suyunun soğan (Allium cepa L.) kök ucu hücrelerinde genotoksik etkisinin değerlendirilmesi. Marmara Fen Bilimleri Dergisi, 3: 111-117. DOI:10.7240/marufbd.311079
Karaismailoğlu MC. 2013. Deltamethrin ve quizalofop-p-etil pestisitlerinin Helianthus annuus L. (ayçiçeği) kök ucu hücreleri üzerine mutajenik etkilerinin araştırılması. Master’s Thesis. Karadeniz Technical University, Trabzon, Turkey.
Karaismailoğlu MC. 2015. Investigation of the potential toxic effects of prometryne herbicide on Allium cepa root tip cells with mitotic activity, chromosome aberration, micronucleus frequency, nuclear DNA amount and comet assay. Caryologia, 68: 323-329
Karaismailoğlu MC. 2016. The evaluation of the genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of pyriproxyfen Insecticide on Allium cepa somatic chromosomes with mitotic activity, chromosome abnormality and micronucleus frequency. Turk J Life Sci. 1/2:065-069
Karaismailoğlu MC. 2017. Investigation of the antimitotic and antimutagenic effects of methanolic extracts of Pyracantha coccinea. Turk J Life Sci. 2/1:110-116
Kaymak F. 2005. Cytogenetic effects of maleic hydrazide on Helianthus annuus L. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences 8: 104-108.
Metin M, Bürün B. 2008. Cytogenetic effects of Urginea maritima L. aqueous extracts on the choromosomes by using allium test method. Caryologia Vol.61 (4): 342-348.
Oloyede A, Okpuzor J, Omidiji O. 2009. Cytological and toxicological properties of a decoction used for managing tumors in Southwestern Nigeria. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences 12(4): 383-387.
Ogueke CC, Ogbulie JN, Okoli IC, Anyanwu BN. 2007. Antibacterial activities and toxicological potentials of crude ethanolic extracts of Euphorbia hirta. The Journal of American Science, 3(3):11-16.
Oney-Birol S, Gündüz F. 2019. L- Karnitinin sitotoksik ve genotoksik etkilerinin Allium cepa kök ucu testi ile değerlendirilmesi. KSU J. Agric Nat 22(4): 650-658. DOI:10.18016/ksutarimdoga.vi.526634
Öncüer C. 2004. Tarımsal zararlılarla savaş yöntemleri ve ilaçları. Adanan Menderes Üniversitesi Yayınları No.19: 260-299 Aydın, Türkiye.
Özbilgin S, Çitoğlu Saltan G. 2012. Uses of some Euphorbia species in traditional medicine in Turkey and their biological activities. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 9 (2), 241-256.
Pandey H, Kumar V, Roy BK. 2014. Assessment of genotoxicity of some common food preservatives using Allium cepa L. as a test plant. Toxicology Reports 1(C): 300-308. DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2014.06.002
Pirdal G, Liman R. 2019. Cytotoxic and genotoxic assessment of 2-chloropyridine using Allium cepa anatelophase and comet test. Mediterr Agric Sci 32(2): 193-199. DOI: 10.29136/mediterranean.539752
Rank J. 2003. The method of allium anaphase telophase chromosome assay. Ekologija 1:38-42,
Rosculete E, Olaru AL, Rosculete CA, Bonciu E. 2020. Assessment of cytological effects of food preservative potassium metabisulphite to Allium cepa. American Journal of Plant Sciences, 11, 11-23. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2020.111002
Shi Q-W, Su X-H, Kiyota H. 2008. Chemical and pharmacological research of the plants in genus Euphorbia. Chem. Rev. 108, 4295–4327. American Chem. Soc. Pub. on Web 09/25/2008.
Sivas H, Gökbayrak S. 2011. Investigation of cytotoxic effects of pyridine in root meristem cells of onion (Allium cepa). Biological Diversity and Conservation, 4/2:92-98.
Türkoğlu Ş. 2007. Genotoxicity of five food preservatives tested on root tips of Allium cepa L. Mutation Research/Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis 626(1-2):4-14. DOI: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2006.07.006
Wang X, Liu L, Zhu R, Kang T, Tong L, Xie H, Wang H. 2006. Cytotoxic activities of some selected medicinal plants of the genus Euphorbia. J. of Med.Plants Res., 5(31): 6766-6769.
Yüzbaşıoğlu D. 2003. Cytogenetic effects of fungucide afugan on the meristematic cells of Allium cepa L. The Japan Mendel Society Cytologia 68 (3): 237-243.
Zhang W, Guo YW. 2006. Chemical studies on the constituents of the chinese medicinal herb Euphorbia helioscopia L. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 54 (7) 1037—1039.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2020 Mert Met?n

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- Copyright on any open access article in a journal published byCaryologia is retained by the author(s).
- Authors grant Caryologia a license to publish the article and identify itself as the original publisher.
- Authors also grant any third party the right to use the article freely as long as its integrity is maintained and its original authors, citation details and publisher are identified.
- The Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 formalizes these and other terms and conditions of publishing articles.
- In accordance with our Open Data policy, the Creative Commons CC0 1.0 Public Domain Dedication waiver applies to all published data in Caryologia open access articles.