Chromosome Mapping of Repetitive DNAs in the Picasso Triggerfish (Rhinecanthus aculeatus (Linnaeus, 1758)) in Family Balistidae by Classical and Molecular Cytogenetic Techniques
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36253/caryologia-1731Keywords:
Triggerfish, Chromosome, Repetitive sequences, Fish cytogeneticsAbstract
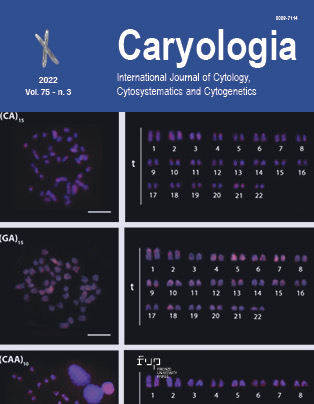
This work presents the cytogenetic analysis conducted on the Picasso triggerfish (Rhinecanthus aculeatus (Linnaeus, 1758)) from Thailand. Mitotic chromosomes were prepared from the anterior kidney. The cell suspensions were harvested by in vivo colchicine treatment. The present study includes the chromosomal investigation on R. aculeatus, using conventional (Giemsa staining, Ag-NOR and C-banding) and molecular approaches (in situ mapping of five different repetitive DNA classes including 18S rDNA, 5S rDNA, (CA)15, (GA)15 and (CAA)10 as markers.) The results showed that R. aculeatus has karyotypes formed exclusively by telocentric chromosomes (44t; NF=44). The C-positive heterochromatic blocks are preferentially located in the centromeric and telomeric regions of some chromosomal pairs. The Ag-NOR sites occupy the interstitial position of the long arms of the largest telocentric pair (pair 1). The exclusive location of the major ribosomal sites in these pairs was confirmed by hybridization with 18S rDNA probes. However, the 5S rDNA genes are not located on 18S rDNA-bearing chromosomes, but instead located exclusively in the subcentromeric region of pair 4. The mapping of (CA)15, (GA)15 and (CAA)10 microsatellites are sparsely dispersed along all the chromosomes. The karyotype formula of R. aculeatus is 2n (44) = 44t.
Downloads
References
Allen, G.R., Erdmann, M.V. & Purtiwi, P.D. (2017). Descriptions of four new species of damselfishes (Pomacentridae) in the Pomacentrus philippinus complex from the tropical western Pacific Ocean. Journal of the Ocean Science Foundation 25:47–76.
Almeida-Toledo, L.F. (1985). As regiões organizadoras do nucléolo em peixes. Cienc. Cult. 37: 448–453.
Arai, R. (2011). Fish Karyotypes: a check list. Tokyo: Springer.
Arai, R. & Nagaiwa, K. (1976). Chromosomes of tetraodontiform fishes from Japan. Bull. Natl. Sci. Mus. Tokyo 2: 59–72.
Cioffi, M.B., Molina, W.F., Moreira-Filho, O., & Bertollo, L.A.C. (2011). Chromosomal distribution of repetitive DNA sequences high- lights the independent differentiation of multiple sex chromo- somes in two closely related fish species. Cytogenet Genome Res 134:295–302.
de Lima, L.C.B., Martinez, P.A. & Molina, W.F. (2011). Cytogenetic characterization of three Balistoidea fish species from the Atlantic with inferences on chromosomal evolution in the families Monacanthidae and Balistidae. Comparative Cytogenetics 5(1): 61–69.
Getlekha, N., Molina, W.F., Cioffi, M.B., Yano, C.F., Maneechot, N., Bertollo, L.A.C., Supiwong, W. & Tanomtong, A. (2016a). Repetitive DNAs highlight the role of chromosomal fusions in the karyotype evolution of Dascyllus species (Pomacentridae, Perciformes). Genetica 144:203–211.
Getlekha, N., Cioffi, M.B., Yano, C.F., Maneechot, N., Bertollo, L.A.C., Supiwong, W., Tanomtong, A. & Molina, W.F. (2016b). Chromosome mapping of repetitive DNAs in sergeant major fishes (Abudefdufinae, Pomacentridae): a general view on the chromosomal conservatism of the genus. Genetica 144:567–576.
Getlekha, N., Cioffi, M.B., Maneechot, N., Bertollo, L.A.C., Supiwong, W., Tanomtong, A.and Molina, W.F. (2018). Contrasting Evolutionary Paths Among Indo-Pacific Pomacentrus Species Promoted by Extensive Pericentric Inversions and Genome Organization of Repetitive Sequences. Zebrafish. 15(1): 45–54.
Gustavo, S. L. & Molina, W. F. (2004). Inferências sobre a evolução cariotípica em Balistidae, Diodontidae, Monacanthidae e Tetraodontidae (Pisces, Tetraodontiformes). Exemplo de extensa diversificação numérica. M.Sc. Thesis. Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil.
Gustavo, S. L. & Molina, W. F. (2005). Karyotype diversifification in fishes of the Balistidae, Diodontidae and Tetraodontidae (Tetraodontiformes). Caryologia 58: 229–237.
Kitayama, E. & Ojima, Y. (1984). A preliminary report on the phylogeny of five balistid fish in terms of several chromosome banding techniques in combination with a statistical analysis. Proc. Jpn. Acad., Ser. B, Phys. Biol. Sci. 60: 58–61.
Marques, D.A., Lucek, K., Meier, J.I,. Mwaiko, S., Wagner, C.E., Excoffier, L. & Seehausen, O. (2016). Genomics of rapid incipient speciation in sympatric threespine stickleback. PLOS Genetics 12:2:e1005887.
Molina, W.F. & Galetti, P.M. (2002). Robertsonian rearrangements in the reef fish Chromis (Perciformes, Pomacentridae) involving chromosomes bearing 5S rRNA genes. Genet Mol Biol 25:373–377.
Molina, W.F., Martinez, P.A., Bertollo, L.A. & Bidau, C.J. (2014a). Evidence for meiotic drive as an explanation for karyotype changes in fishes. Mar Genomics 15:29–34.
Molina, W.F., Martinez, P.A., Bertollo, L.A. & Bidau, C.J. (2014b) Preferential accumulation of sex and Bs chromosomes in biarmed karyotypes by meiotic drive and rates of chromosomal changes in fishes. An Acad Bras Ciênc 2014b;86:4:1801–1812.
Montanari, S.R., Hobbs, J.P., Pratchett, M.S. and van Herwerden, L. (2016). The importance of ecological and behavioural data in studies of hybridisation among marine fishes. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries 26:181–198.
Nelson, J.S., Grande, T.C. & Wilson, M.V.H. (2016) Fishes of the World. 5th ed. Hoboken : John Wiley and Sons, Inc.
Sharma, O.P., Tripathi, N.K. & Sharma, K.K. (2002). A review of chromosome banding in fishes. In: Sobti, R. C., ed. Some aspects of chromosome structure and functions. Narosa Publishing House, New Delhi.
Supiwong, W., Tanomtong, A. Jumrusthanasan, S. & Sanoamuang, L. (2013). Standardized Karyotype and Idiogram of Titan Triggerfish, Balistoides viridescens (Tetraodontiformes, Balistidae) in Thailand. CYTOLOGIA 78(4):345–351.
Takai, A. & Ojima, Y. (1988). Karyotype and banding analyses in a balisted fish, Balistoides viridescens “gomamongara.” Chromosome. Inform. Serv. 45: 25–27.
Takai, A. & Ojima, Y. (1987). Comparative chromosomal studies in three balistid fishes. La Kromosomo, II 47/48: 1545–1550.
Thode, G., Amores, A., & Martinez, G. (1994). The karyotype of Balistes carolinensis Gmelin (Pisces, Tetraodontiformes), a specialized species. Caryologia 47: 257–263.
Vitturi, R., Catalano, E., & Colombera, D. (1992). Karyotype analyses of the teleostean fish Balistes carolinensis and Lophius piscatorius suggest the occurrence of two different karyoevolutional pathways. Biol. Zent. Bl. 111: 215–222.
Vitturi, R., Zava, B., Catalano, E., Maiorca, A. & Macaluso, M. (1988). Karyotypes in five Mediterranean teleostean fishes. Biol. Zent. Bl. 107: 339–344.
Yano, C.F, Bertollo, L.A.C. & Cioffi, M.B. (2017). Fish-FISH: Molecular Cytogenetics in Fish Species. In: Fluorescence in situ Hybridization (FISH)- Application Guide. 2nd edn, Liehr, T. (ed) Springer, Berlin, pp. 429–444.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Kamika Sribenja, Alongklod Tanomtong, Nuntaporn Getlekha

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- Copyright on any open access article in a journal published byCaryologia is retained by the author(s).
- Authors grant Caryologia a license to publish the article and identify itself as the original publisher.
- Authors also grant any third party the right to use the article freely as long as its integrity is maintained and its original authors, citation details and publisher are identified.
- The Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 formalizes these and other terms and conditions of publishing articles.
- In accordance with our Open Data policy, the Creative Commons CC0 1.0 Public Domain Dedication waiver applies to all published data in Caryologia open access articles.